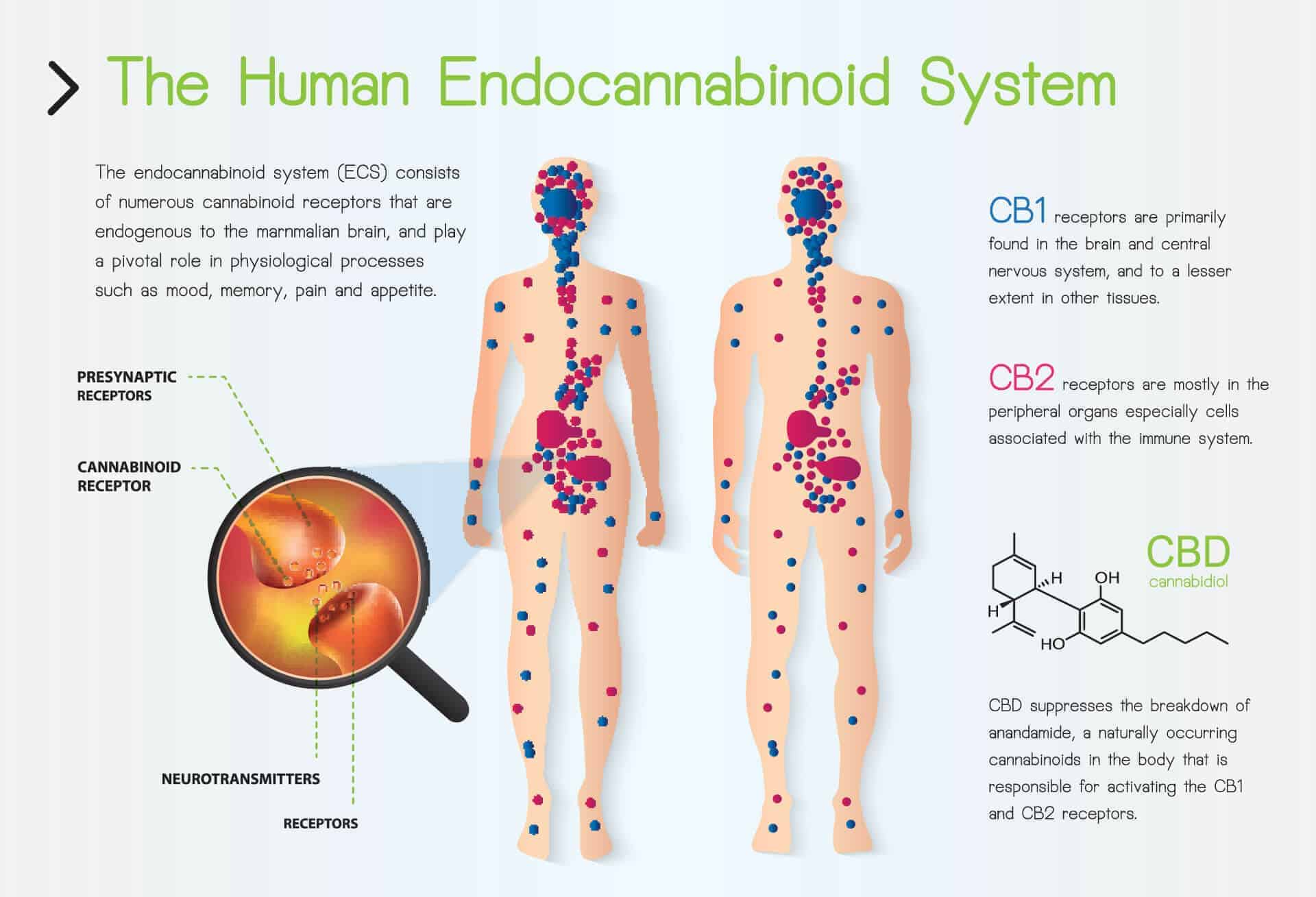
THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM is a biological system first discovered in the late ’80s and early ’90s. The ECS is largely composed of endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes that are believed to help regulate a variety of functions in humans including sleep, mood, memory, appetite, reproduction, and pain sensation.
THE ECS purpose of the function is to create and maintain homeostasis in the body. Homeostasis is the concept that most biological systems are actively regulated to maintain conditions within a narrow range. Our bodies don’t want our temperature to be too hot or too cold, but just right for our cells to maintain optimum performance. The ECS function of homeostasis runs parallel with the balance of the mind, body, and is the physical manifestation of this theory.
The body’s ECS is a vital molecular system for helping maintain homeostasis and for the cells to stay in their Goldilocks zone, “just right”!
The ECS is widespread throughout the animal kingdom. The ECS key components evolved a long time ago, and the ECS can be found in all vertebrate species. The key components of the human endocannabinoid system are cannabinoid receptors, found on the surface of the cells, and endocannabinoids.
Cannabinoid receptors are an important class of cell membrane receptors that are divided into two main groups, CB1 and CB2. They are mostly differentiated by the organs or systems they work within the body.
CB1 is mostly found in the brain. CB1 receptors are mostly associated with psychoactive and euphoric aspects of THC.
CB2 receptors are mostly found within the immune system and blood cells, and secondarily in lesser quantities within the nervous system, liver, gut, muscle, and bone.
Endocannabinoids are molecules that bind and activate the CB1 and CB2 receptors throughout the brain and body. In the human body, the two main endocannabinoids are Anandamide and 2-AG. Anandamide is derived from the Sanskrit word “ananda” which means “joy”, and is often called the bliss molecule. 2-AG is present at high levels in the central nervous system and was first discovered by Raphael Mechoulam in 1994.
Phytocannabinoids are plant produced molecules that bind the cannabinoid receptors in the brain and human body. THC and CBD are the most common of these plant cannabinoids. THC and CBD bind with the CB1 and CB2 receptors just like Anandamide and 2-AG. Cannabis is a medicinal plant that works to activate and empower the endocannabinoid system, which in turn creates homeostasis, and brings balance to the mind-body creating peace and wellness from within.